Copyright © Rogue Amoeba Software, Inc. All rights reserved.
In addition to capturing audio from traditional applications, SoundSource can also capture from certain special sources, as well as hidden background processes which do not appear on your Mac like traditional applications. This includes system services, as well as the occasional command-line tool. Read on for more details.
SoundSource's Add Favorite menu makes it easy to choose popular sources which would otherwise be very difficult to find. This is done through the Special Sources section of the Add Favorite menu, where you can choose:
 Background Sounds
(MacOS 13 and higher)
Background Sounds
(MacOS 13 and higher)
 Finder
Finder
 Notification Center
(MacOS 15 and higher)
Notification Center
(MacOS 15 and higher)
 Siri
(MacOS 13 and higher)
Siri
(MacOS 13 and higher)
 Spoken Content
(MacOS 15 and higher)
Spoken Content
(MacOS 15 and higher)
 System AirPlay Receiver
(MacOS 12 and higher)
System AirPlay Receiver
(MacOS 12 and higher)
 VoiceOver
(MacOS 13 and higher)
VoiceOver
(MacOS 13 and higher)
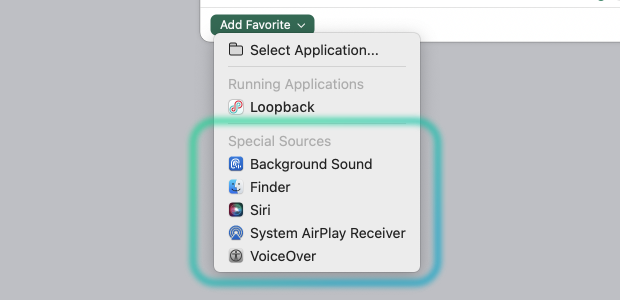
 Background Sounds
Background Sounds
The Background Sounds special source handles background audio played via the Audio section of the Accessibility options of the System Settings app.
com.apple.accessibility.heard
 Finder
Finder
The Finder special source handles any audio played by the Finder, as well as audio produced using the Mac's “Quick Look” functionality.
com.apple.finder
com.apple.quicklook.QuickLookUIService
 Notification Center
Notification Center
The Notification Center special source handles any audio played through the system’s Notification Center, such as alarm sounds produced by MacOS’s “Clock” app.
com.apple.notificationcenterui
 Siri
Siri
The Siri special source handles all the audio from Siri, including both its sound effects and its spoken word audio.
com.apple.CoreSpeech
com.apple.sirittsd
com.apple.Siri
com.apple.CoreSpeech
com.apple.speech.speechsynthesisd
 Spoken Content
Spoken Content
The Spoken Content special source captures audio produced by the system when using text reading (triggered by the Start Speaking command in the Speech menu), as well as audio generated by the Spoken Content options in the system’s Accessibility settings.
Note that while some applications send text-to-speech audio to the system process, others produce it from their own processes. Unfortunately, this means you may need to experiment to determine the exact source of text-to-speech audio. If the Spoken Content special source does not indicate activity, have a look at the application in which the text is being read itself.
This special source was introduced on MacOS 15, where it replaced the previous Text to Speech special source.
com.apple.accessibility.AXVisualSupportAgent
com.apple.Accessibility-Settings.extension
com.apple.speech
com.apple.speech.speechsynthesisd
com.apple.speech.synthesis.SpeechSynthesisServer
com.apple.UniversalAccessControl
 System AirPlay Receiver
System AirPlay Receiver
The System AirPlay Receiver special source handles audio played directly to MacOS via AirPlay, using the system's AirPlay receiving capabilities.
com.apple.controlcenter
 VoiceOver
VoiceOver
The VoiceOver special source handles all the audio from the VoiceOver experience, including both spoken words and sound effects.
com.apple.VoiceOver
com.apple.VoiceOverQuickstart
com.apple.speech.speechsynthesisd
com.apple.VoiceOver
com.apple.VoiceOverQuickstart
com.apple.speech.speechsynthesisd
com.apple.VoiceOver
Due to changes in MacOS, some special sources have been removed from our apps. Details are preserved here.
On older versions of MacOS (MacOS 12 and lower), SoundSource offered a System Speech special source. This handles all audio spoken by the system, including Siri and VoiceOver. Due to the way the system provides this audio, it is merged into one special source. Do note that any adjustment you make to this special source will affect audio from all of these sources.
As a result of change’s made by Apple, it was removed on MacOS 13 and up, with the Siri and VoiceOver special sources serving as replacements.
The Text to Speech special source handles audio played by the system's text reading (triggered by the Start Speaking command in the Speech menu). On MacOS 14, some applications produce audio from their own processes, while others send it to the system process. Unfortunately, this means you may need to pay attention to active applications in SoundSource to determine exactly which application is producing audio. If the Text to Speech special source is not producing audio, pay attention to the application in which the text is being read itself.
(MacOS 12 and lower)
 System Speech
System Speech
Captured Sources
com.apple.CoreSpeechcom.apple.speech.speechsynthesisdcom.apple.VoiceOver
(MacOS 14)
 Text to Speech
Text to Speech
Captured Source
com.apple.accessibility.AXVisualSupportAgent